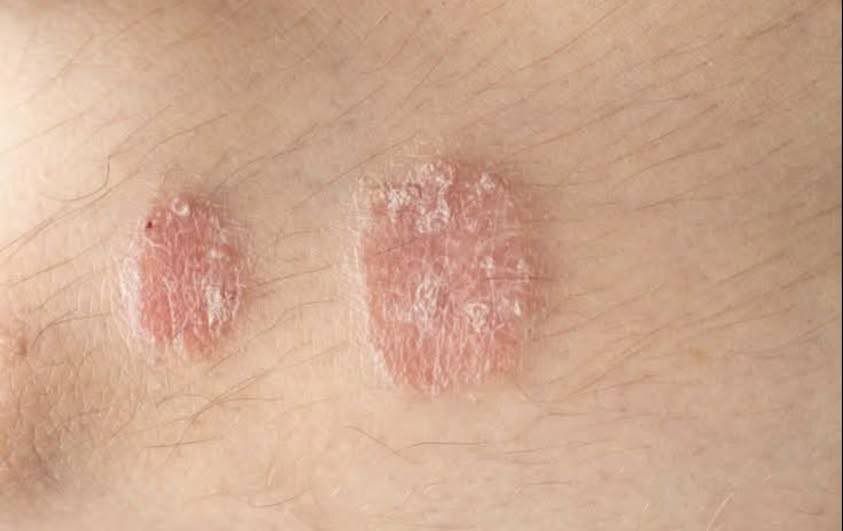
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people around the world. While it’s not contagious, early recognition of its symptoms is important for effective treatment. Understanding the types, causes, and treatment options for psoriasis can help manage the condition better.
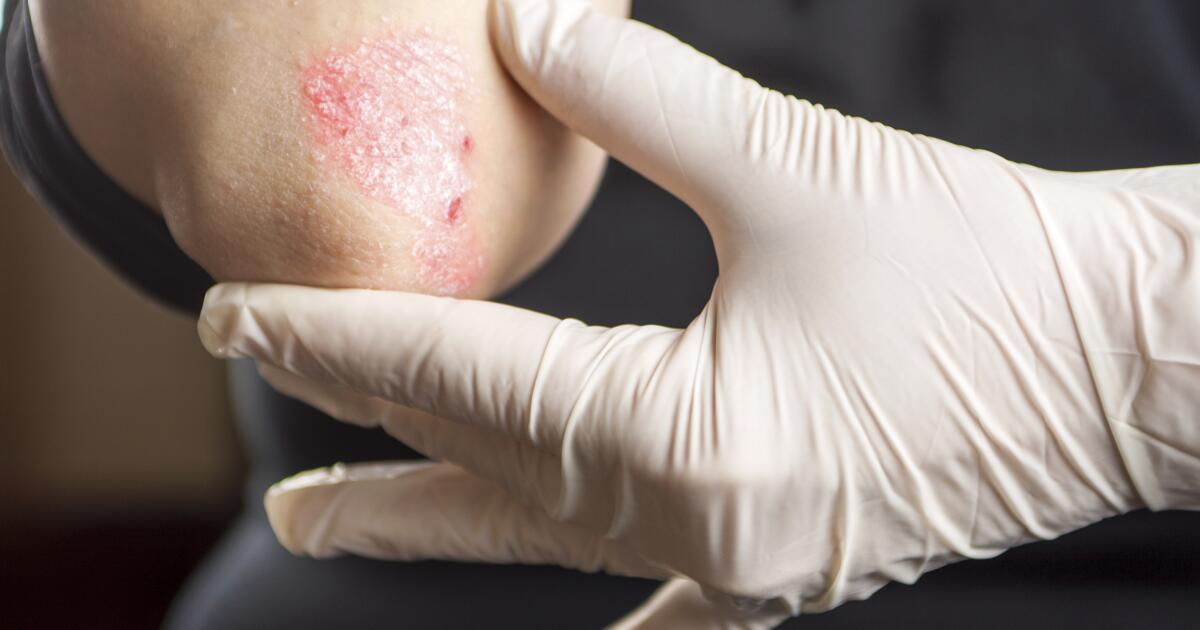
Psoriasis can present itself in different forms, each with distinct characteristics:
- Plaque psoriasis is the most common type. It shows up as red patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales.
- Guttate psoriasis appears as small, drop-shaped spots. It’s often triggered by infections like strep throat.
- Pustular psoriasis is identified by blisters filled with pus, sitting on top of red and swollen skin.
- Inverse psoriasis causes smooth, red patches in moist areas of the body, such as skin folds.
These various types of psoriasis highlight the diverse ways the condition can affect the skin, making it important to identify the specific type for appropriate care.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/psoriasis-symptoms-GettyImages-1401047657-9a56ec1fd8934e6cb549dcf09640ae38.jpg)
The causes of psoriasis involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid cell turnover and buildup.
Several factors can trigger or worsen psoriasis, including:
- Stress
- Infections
- Cold weather
- Certain medications
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VerywellHealth_TypesofPsoriasis_colorv1-2b61e1b6ecbe4fe699ffc08759208d26.png)
Treatment for psoriasis often depends on the severity and type of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Topical treatments like creams and ointments to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
- Phototherapy, where skin is exposed to natural or artificial light to improve symptoms.
- Systemic medications for severe cases, which affect the entire body.
Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are key to managing psoriasis. If you notice persistent skin changes, consult a healthcare provider to explore the best treatment plan for your situation.

Psoriasis may be a lifelong condition, but with proper management, many people can keep their symptoms under control and maintain a good quality of life.
